O-Rings
Description of O-Rings
O-rings are mostly used as static seals in between flanges or joint sealing. O-rings offer an efficient and economical sealing element for a wide range of static or dynamic applications and can be used to seal practically all liquid and gaseous media. Positioned within a designated groove, the O-ring undergoes compression upon assembly between two or more parts, effectively sealing the interface and preventing fluid or gas leakage. Widely favored in mechanical designs, O-rings boast simplicity in fabrication, cost-effectiveness, and straightforward mounting requirements.
Function and Working Principle of O-Rings
As the name suggests, O-rings resemble doughnuts or torus shapes and are designed to create a tight seal between two components. Their primary function is to prevent the leakage of liquids or gases. Unlike traditional gaskets, O-rings are preferred in high-pressure environments where other types may fail.
Essentially, O-ring seals are placed in a groove between two mating surfaces. Made from elastomeric materials, they compress to form a secure seal when the surfaces are joined together.
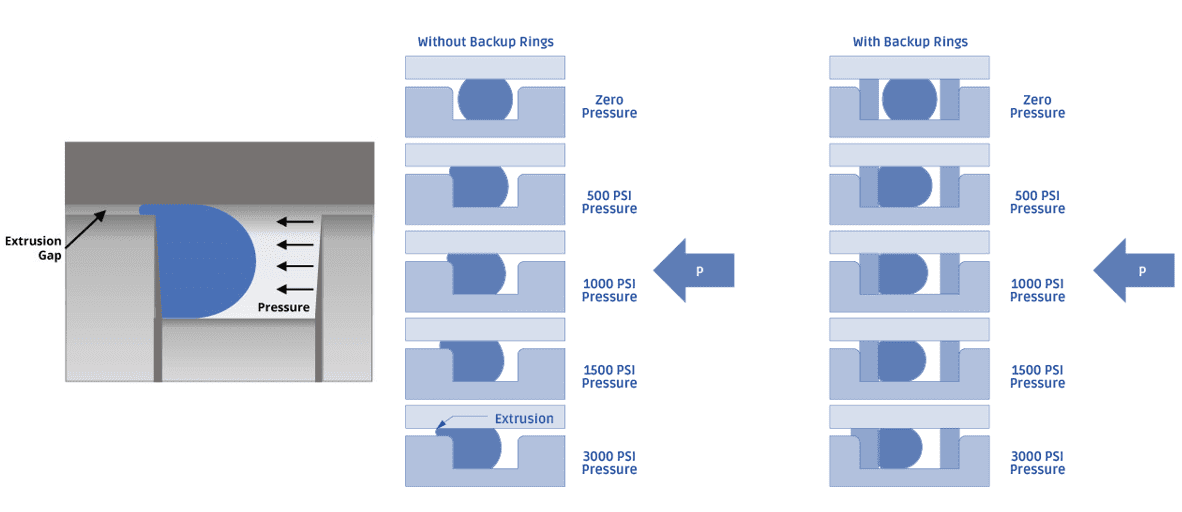
Increased internal pressure on the seal causes it to compress further within the groove, enhancing its sealing effectiveness. However, excessive pressure or dynamic loads can lead to seal failure. Therefore, it's crucial to select the right O-ring material, size, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance.
Think of the rubber in the seal as a thick, sticky liquid. It moves under pressure to block the flow of less thick liquids. The rubber adjusts to differences in the parts and stays sealed because it remembers its shape.
This video by Mykin Inc explains the working principle of an O-ring in an easy fashion.
Advantages of O-Rings
Suitable for a wide range of pressure, tolerance, and temperature
Easy to use
Easy to install and does not cause damage to the system
Light-weight and compact size
O-ring failure can be easily identified
Cost-effective
Applications of O-Rings
Aerospace and aviation: aircraft engines, hydraulic systems, and other critical components
Medical devices: medical equipment such as syringes, pumps, and valves
Plumbing: pipes, faucets, valves, and other plumbing components to prevent leaks
Hydraulics and pneumatics: create a seal between moving parts such as cylinders, actuators, and pistons
Food and beverage processing: processing equipment to prevent contamination and ensure hygiene
Electronics: electronic components such as connectors and switches to prevent moisture and dust from entering
Common household applications: Doors, windows, and containers to prevent leaks and maintain airtight or watertight seals
O-Rings Application Industries
-

Chemical Processing, Oil and Gas Industry
-

Pumps, Motors and Gearboxes
-

Automotive Industry
-

Machine Tools Industry
Product Features of O-Rings
Static sealing application
Pressure up to 100 Bar & up to 300 Bar with special material
Materials Nitrile (Buna), Neoprene, Ethylene Propylene (EPDM Rubber), Silicone, Fluorocarbon (Viton), and PTFE (Teflon)
Temperature range -40°C to 220°C
Various profiles are available for different applications
Cost-effective solution